
| Palaeos: |  |
Glossary |
| EUKARYA | Glossary C-E |
| Page Back | Unit Back | Unit Home | References | Glossary | Pieces |
| Page Next | Unit Next | Life | Dendrogram | Taxon Index | Time |
Calymma: in radiolarians, same as ectoplasm.
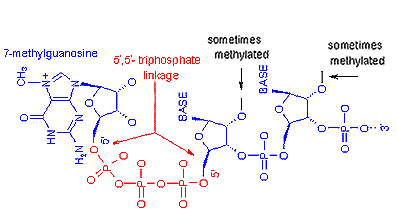 cap,
5': "The 5' cap is a distinctive feature of eukaryotic mRNA. The cap
consists of 7-methyl guanosine linked via an inverted 5'-5' triphosphate bridge
to the initiating nucleoside of the transcript. Cellular mRNAs are capped via
three enzymatic reactions. (i) The 5' triphosphate end of the nascent pre-mRNA
is hydrolyzed to a diphosphate by RNA 5' triphosphatase, (ii) the diphosphate
RNA end is capped with GMP by RNA guanylyltransferase, and (iii) the GpppN cap
is methylated by RNA (guanine-N7) methyltransferase." Hausmann
et al. (2002). The capped end of the mRNA is thus, protected
from exonucleases and more importantly is recognized by specific proteins of the
translational machinery.
cap,
5': "The 5' cap is a distinctive feature of eukaryotic mRNA. The cap
consists of 7-methyl guanosine linked via an inverted 5'-5' triphosphate bridge
to the initiating nucleoside of the transcript. Cellular mRNAs are capped via
three enzymatic reactions. (i) The 5' triphosphate end of the nascent pre-mRNA
is hydrolyzed to a diphosphate by RNA 5' triphosphatase, (ii) the diphosphate
RNA end is capped with GMP by RNA guanylyltransferase, and (iii) the GpppN cap
is methylated by RNA (guanine-N7) methyltransferase." Hausmann
et al. (2002). The capped end of the mRNA is thus, protected
from exonucleases and more importantly is recognized by specific proteins of the
translational machinery.
Capsule: in radiolarians, a fibrous spherical partition of the cytoplasm which divides the cell into intra- and extracapsular spaces, effectively creating a three-compartment cell (nucleoplasm, endoplasm & ectoplasm).
Carboxysome: another cyanobacterial structure adopted by some algae. These are polyhedral, protein-covered bodies, about 120 nm in diameter, packed with RuBisCO, which accounts for about 60% of the carboxysomal protein content. Cannon et al. (2001).
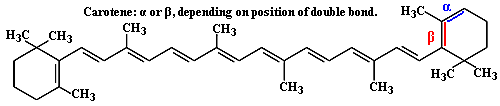 Carotene:
an accessory photosynthetic pigment. The most common forms are alpha and
beta carotene, which differ in the position of a one double bond, as shown in
the image.
Carotene:
an accessory photosynthetic pigment. The most common forms are alpha and
beta carotene, which differ in the position of a one double bond, as shown in
the image.
Carotenoid: any of a family of carotene-like pigments.
Cellulose: a polymer of glucose. Poly(β1→4)-D-glucose. Starch is chemically identical, but has an alpha linkage between adjacent glucose monomers.
Centrosomal plaque: see plaque, centrosomal.
Chaperonin (often abbreviated Cpn): "chaperone" proteins which assist in the folding of other newly synthesized proteins.
Chitin: a polymer of repeating sugar molecules (a slightly modified glucose, N-acetylglucosamine). See image. Chitin is also frequently found in a cross-linked form, alpha chitin, as in the armor of arthropods. See image. Chitin is the material which makes up the exoskeleton of insects and, in more or less modified form, in almost all arthropods. Significantly, it is also found in the radular "teeth" of mollusks, the setae (bristles) and jaws of annelid worms, and the cell walls of Fungi. So, this is exceedingly ancient stuff, possibly predating the split between bacteria and metazoans.
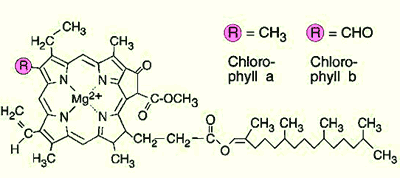 Chlorophyll:
a widely dispersed photosynthetic pigment, particularly effective in red and
blue light (it reflects the mid-range green wavelengths, which is why it appears
green to our eyes). Note that chlorophylls a and b differ only in
the substitution of a methoxy for a methyl ligand in one position.
Chlorophyll:
a widely dispersed photosynthetic pigment, particularly effective in red and
blue light (it reflects the mid-range green wavelengths, which is why it appears
green to our eyes). Note that chlorophylls a and b differ only in
the substitution of a methoxy for a methyl ligand in one position.
Chuar Group: Neoproterozoic of northern Arizona (USA), with exposures along the Grand Canyon. Composed of the Galeros and Kwagunt Formations (older to younger). The upper limit is constrained to be about 742 My old. Porter & Knoll (2000).
Cilium: a short flagellum found, unsurprisingly, in the Ciliophora. Cilia and flagella have the same basic structure.
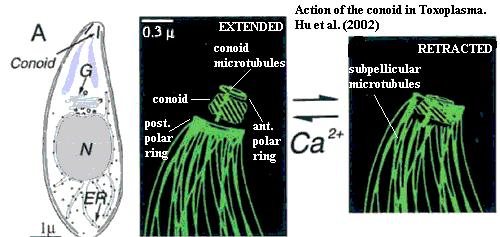 Conoid:
a structure shaped like a truncated cone, located in the apical complex of some Apicomplexa.
When present, it is located in the center of the polar rings, with the short
narrow end pointing anteriorly. The conoid intermittently protrudes beyond
the apical end of the microtubules. Protrusion of the conoid is sensitive
to parasite cytoplasmic calcium concentration. The conoid consists of
fibers wound into a spiral like a compressed spring. This system of fibers
is composed of a novel polymer of tubulin. Hu
et al. (2002).
Conoid:
a structure shaped like a truncated cone, located in the apical complex of some Apicomplexa.
When present, it is located in the center of the polar rings, with the short
narrow end pointing anteriorly. The conoid intermittently protrudes beyond
the apical end of the microtubules. Protrusion of the conoid is sensitive
to parasite cytoplasmic calcium concentration. The conoid consists of
fibers wound into a spiral like a compressed spring. This system of fibers
is composed of a novel polymer of tubulin. Hu
et al. (2002).
Cpn70 (a/k/a Hsp70): a class of "chaperone" proteins which assist in the folding of other newly synthesized proteins. Cpn70 proteins have a particular target preference for hydrophobic amino acid sequences.
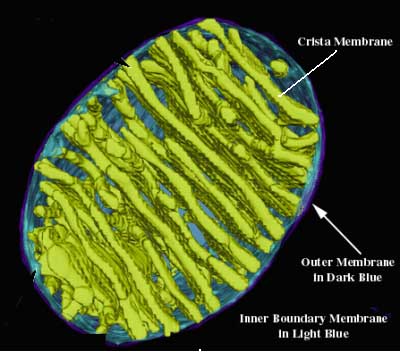 Crista (pl. cristae):
(1) of mitochondria, folds in the internal membrane
of the mitochondrion which gives the organelle its characteristic
appearance. This is the site of the electron transport chain in oxidative
metabolism. The cristae, therefore, serve as the physical link between the
tricarboxylic acid cycle and oxidative phosphorylation (ATP synthesis). See
also Mitochondrion - Wikipedia.
(2) more generally, a crest (its literal meaning in Latin) or
ridge.
Crista (pl. cristae):
(1) of mitochondria, folds in the internal membrane
of the mitochondrion which gives the organelle its characteristic
appearance. This is the site of the electron transport chain in oxidative
metabolism. The cristae, therefore, serve as the physical link between the
tricarboxylic acid cycle and oxidative phosphorylation (ATP synthesis). See
also Mitochondrion - Wikipedia.
(2) more generally, a crest (its literal meaning in Latin) or
ridge.
Cryptobiotic: capable of surviving adverse conditions by maintaining suspended animation, as in a spore-like, desiccated form.
Cryptoxanthin: a carotenoid light-sensitive pigment. Alpha and beta cryptoxanthin are identical to alpha and beta carotene, respectively, except that the invariant cyclohexene ring has a hydroxyl ligand in the trans position (relative to the long chain).
Cyanelle: in essence, a chloroplast. This term is used in reference to the chloroplasts of glaucophytes and a few other types because the structure is so primitive that it includes a number of morphological and genetic features otherwise found only in cyanobacteria. Steiner et al. (2001).
Cytoproct: in Ciliophora, a permanent surface pore for the ejection of waste.
Cytopyge: same as cytoproct.
Cytostome: the feeding groove or "mouth" of Ciliophora.
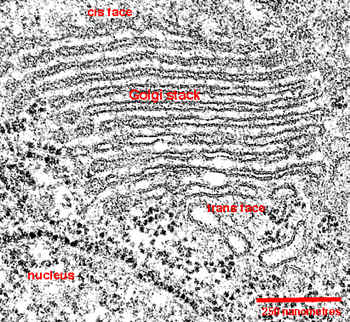 Dictyosome:
botanical term for a structure which is the functional equivalent of the animal
Golgi apparatus. "A stack of thin vesicles held together in a flat or
cup-shaped array which receive vesicles from endoplasmic reticulum along their
forming face, then modify the material in the vesicle lumen or synthesize new
material. Vesicles swell and are released from the maturing face." Botany- Interactive Glossary definition for 'dictyosome'.
The point is that protein products are both made and packaged in a vesicle by
this apparatus. In plants, the vesicle is exported from the cell.
Dictyosome:
botanical term for a structure which is the functional equivalent of the animal
Golgi apparatus. "A stack of thin vesicles held together in a flat or
cup-shaped array which receive vesicles from endoplasmic reticulum along their
forming face, then modify the material in the vesicle lumen or synthesize new
material. Vesicles swell and are released from the maturing face." Botany- Interactive Glossary definition for 'dictyosome'.
The point is that protein products are both made and packaged in a vesicle by
this apparatus. In plants, the vesicle is exported from the cell.
Diplokaryon: two cell nuclei in close physical association.
Ectoplasm: in radiolarians, the outer cytoplasmic region outside the cytoplasmic capsule, a fibrous partition of the cytoplasm. This extracapsular ectoplasm usually contains feeding and gas vacuoles and symbiotic zooxanthellae. Opposite of endoplasm.
Elongation factor 1α (usually abbreviated EF-1α): Elongation factors are proteins involved in mRNA translation in animals. This particular type is of unusual interest because its homologue appears to be closely associated with microtubule assembly in a variety of protists and plants.
Endoplasm: in radiolarians, the inner cytoplasmic region inside the cytoplasmic capsule, a fibrous partition of the cytoplasm. This intracapsular endoplasm usually contains the major cytoplasmic organelles, nuclei and Golgi apparatus. Opposite of ectoplasm.
Endospore: in the Microsporidia, a protective coat of chitin located between the outer protein exospore and the cell membrane.
Epiplasm: a fibrous material which forms part of the ciliophoran pellicle.
Excavate: as an adjective, "possessing a ventral feeding groove that collects suspended particles driven into it by the beating of a posterior flagellum." Simpson et al. (2002: 239). The "excavate hypothesis" is the hypothesis that the excavate taxa are monophyletic, vis. the taxon Excavata.
Exospore: in the Microsporidia, an external protein capsule external to both the chitinous endospore and the plasma membrane.
Extracapsular: in radiolarians, the outer cytoplasmic region outside the capsule, a fibrous partition of the cytoplasm. The extracapsular cytoplasm is often referred to as the ectoplasm. It usually contains feeding and gas vacuoles and symbiotic zooxanthellae.
Extrusome: An ejectable organelle, located within the cell; the contents of which can be extruded. Extrusomes may be used for protection or prey capture. Extrusomes are frequently located at more or less fixed locations adjacent to "oral" structures. In Ciliophora, the extrusomes can rapidly eject short threadlike structures. These extrusomes function in predation, defense, and in forming cysts in various ciliates. Introduction to the Ciliata.
| Page Back | Page Top | Unit Home | Page Next |