
illustration by Dmitry Bogdanov (Wikipedia)
| Ichthyosauria | ||
| The Vertebrates | Ophthalmosauria |
| Vertebrates Home | Vertebrate | Vertebrate |
|
Abbreviated Dendrogram
Diapsida
╞═Younginiformes
└─┬─┬?─Thalattosauria
│ └─○Ichthyopterygia / Ichthyosauria
│ ├─Utatsusaurus
│ └─┬─Ichthyosauria
│ └─┬─Merriamosauria
│ └─┬─Euichthyosauria
│ └─┬─Parvipelvia
│ ├─Eurhinosauria
│ └─○Thunnosauria
│ ├─Stenopterygius
│ └─┬─Ichthyosaurus
│ └─○Ophthalmosauria
│ ├─Brachypterygius
│ └─┬─Ophthalmosaurus
│ └─Platypterygius
└─┬─Lepidosauromorpha
└─Archosauromorpha |
Overview |
 |
| Platypterygius kiprijanoffi (Early Cretaceous, Russia) illustration by Dmitry Bogdanov (Wikipedia) |
 Ophthalmosauria: Aegirosaurus, Brachypterygius, Caypullisaurus, Nannopterygius, Ophthalmosaurus, Otschevia, Paraophthalmosaurus, Platypterygius, Plutoniosaurus, Simbirskiasaurus, Undorosaurus (= Ophthalmosauridae)
Ophthalmosauria: Aegirosaurus, Brachypterygius, Caypullisaurus, Nannopterygius, Ophthalmosaurus, Otschevia, Paraophthalmosaurus, Platypterygius, Plutoniosaurus, Simbirskiasaurus, Undorosaurus (= Ophthalmosauridae)
Range: Middle Jurassic to Late Jurassic
Phylogeny: Thunnosauria : Ichthyosaurus + * : Ophthalmosauria : Brachypterygius + (Ophthalmosaurus + Platypterygius).
Characters: extra zeugopodial element anterior to radius, with associated extra digit.
 |
| Ophthalmosaurus icenicus, from the Oxford Clay, in Peterborough, England. Photo by Captmondo (Wikipedia). |
Comments: The only middle Jurassic through to Cretaceous ichthyosaurs. Cladistic analysis by Motani 2000 and Maisch & Matzke 2000 show the Ophthalmosaurs to be the most specialised and advanced ("derived" to use the technical cladistic term) of all the fish-like Ichthyosaurs. However Lawrence, 2008 used a species level analysis in which the Ophthalmosauria appear as a paraphyletic basal group between the basal Parvipelvian Suevoleviathan and a paraphyletic Eurhinosauria.
Links: Charmouth 180 million years BC and the Ichthysaur.; Geology Field Trip Guide - Kimmeridge, Dorset - Kimmeridge Clay Fossils; Diving; Untitled Document JVP abstract); Re- NEW RHYNCHOSAUR & TEMNOSPONDYLS questioning monophyly). ATW030613.
Synonyms: Grendelius and Otschevia
Late Jurassic (Early Kimmeridgian to Late Tithonian), known from England and European Russia (central Laurasia).
Ophthalmosauria : (Ophthalmosaurus + Platypterygius) + *
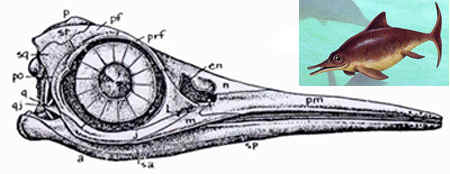
Large ichthyosaur, exceeding 5m in total length, skull with moderately large orbit, large, well developed dentition retained in adults , maxilla very long anterior to external naris ( Maisch & Matzke 2000 p.79), very broad forepaddles, hence the name (latipinnate) (von Zittel & Eastman, 1932? p.281)
Comments: the most basal of the Ophthalmosaurs. (Motani 1999b). MAK100925
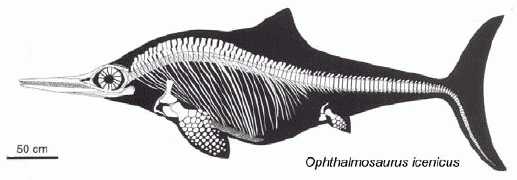 |
| Ophthalmosaurus icenicus, Middle Jurassic (Callovian), England and France, representing the Thunnosaur type. Length about 4 meters. In contrast to all other (less specialised) ichthyosaurs, the body is more rounded (the streamlined "tear-drop" shape), the dorsal fin high, and the fins (paddles) of the shorter and broader "latipinnate" type (convergent with Mixosaurus). From McGowan and Motani, 2003 |
Middle to Late Jurassic, known from England, France, Russia, Wyoming, and Argentina
Ophthalmosauria : Brachypterygius + (Platypterygius + *)
About 4 meters in length, skull with long snout and very large orbit, postorbital skull segment very short, dentition reduced in adults and only at the anterior tips of the jaws, humerus with three facets of subequal size (Maisch & Matzke 2000 p.78; Storrs et al 2000 p.199)
Comments: Had the largest eyes (more than 220 mm in diameter) for any ichthyosaur in prortion to its body length, may have dives to depths of 500 metres or more (Motani et al 1999). A great number of species, which differ only slightly in details. Clearly this was a very successful animal over an extended period of time. Very streamlined "teardrop" shape
Links: Ophthalmosaurus icenicus - Natural History Museum; BBC - Walking with Dinosaurs - Fact Files; Discovery of the ichthyosaur Ophthalmosaurus (Reptilia) in the Late Jurassic of the Boulonnais; Ophthalmosaurus sp.; Ophthalmosaurus (Portuguese); Dinosaurios: Ophthalmosaurus (Spanish); Wikipedia ATW030613, MAK100920
References: Maisch & Matzke 2000
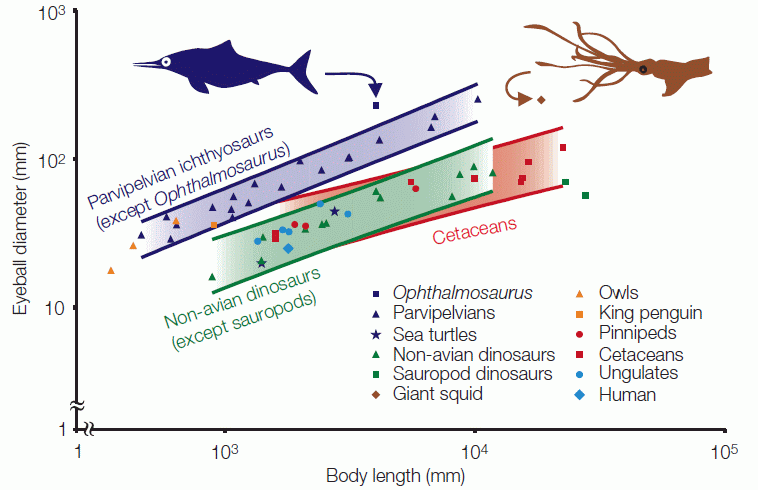 |
| Logarithmic plot of eyeball diameter against body length. Bands show 95% confidence ranges for the least-square regression lines for parvipelvian ichthyosaurs except Ophthalmosaurus, non-avian dinosaurs except sauropods, and cetaceans. Sauropod dinosaurs hade smaller than average eyes, Ophthalmosaurus larger than expected. The giant squid, Architeuthis, has the largest eyes for any extant organism (and as the diagram shows, about equal to the largest ichthyosaur eyes). Eyeball diameters for dinosaurs and ichthyosaurs are based on the external diameter of the sclerotic rings. From Motani et al 1999. For more information presented in a non-technical manner, see also Ryosuke Motani's page on Eyes of ichthyosaurs |
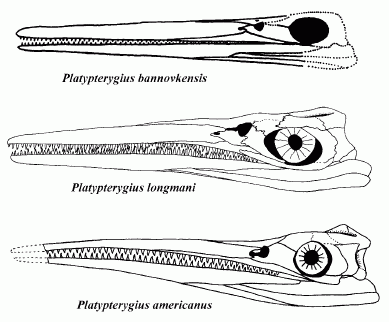 |
| Skull reconstructions of three species of Platypterygius (not to scale). From top to bottom, P. bannovkensis, P. longmani, and P. americanus. Drawings from Maisch & Matzke 2000 p.119. |
Cretaceous, cosmopolitan
Ophthalmosauria : Brachypterygius + (Ophthalmosaurus + *)
average size 5 meters long, but larger species upto 9 meters, skull over 1 meter long in adults, long and slender snout, small orbit, teeth massive with square roots. first three cervical vertebrae fused, tail fin relatively low, the body is generally long, longer flippers than other members of the group
Comments: The most derived of the Ophthalmosaurs, and the only currently recognized genus of Cretaceous ichthyosaurs. The best-known species are Platypterygius longmani from the Aptian of Queensland and Platypterygius americanus from the Early Cretaceous of Wyoming. The type-species, P. platydactylus was originally known from a fairly complete skeleton but this was destroyed in World War II. Arkhangelsky 1998 has divided the genus into four subgenera, Pervushovisaurus, Tenuirostria, Platypterygius and Longirostria, but Maisch & Matzke 2000 reject this approach. Fossilized stomach contents of P. longmani show the diet included fish, cephalopods, and immature turtles. (Kear et al 2003)
Links: Platypterygius, Melbourne Museum: Platypterygius, Platypterygius (Russian, useful page with googl;e translation); Wikipedia, Platypterygius americanus (flickr pghoto - Royal Tyrrell Museum), Ichthyosaurs (includes Opalised fossils)
References: Maisch & Matzke 2000 p.82; Storrs et al 2000 pp.200-1
checked ATW050512