| Cladistics | ||
| Systematics | Monophyly |
| Systematics | ||
| Evolutionary systematics | Molecular phylogeny |
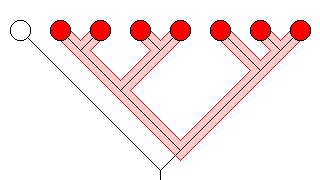
The Monophyletic taxon,also called a clade, is the building block of the cladistic system of taxonomy. It refers to any group of organisms that includes the most recent common ancestor of all those organisms and all the descendants of that common ancestor.
Examples: Insects, Vertebrates, Mammalia, Angiosperms, etc, etc.
A definition of monophyly, from Glossary of Phylogenetic Systematics by Günter Bechly:
"monophyletic group (= monophylum): In a hierarchical system of descent, an ancestor (stem-species) and all of his descendants (descendant species) together form a closed community of descent that is called a monophyletic group (sensu HENNIG; = holophyletic group sensu ASHLOCK) or monophylum. Monophyletic groups can be discovered (not defined!) by synapomorphies. The term monophyly is always referring to groups of hierarchically reproducing entities (species) and consequently can not be applied to (or within) a single biospecies or even to a single organism..."