|
|
Cosmic Evolution |
| Cosmic Evolution |
Cosmic Evolution |
Cosmic Evolution
The Big Picture

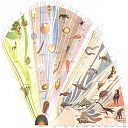
Elaborate diagram by Erich Jantsch presenting a sort of phylogeny of everything, showing the evolution of abiotic matter, life, and mind in terms of progressive stages (or symmetry breaks) of cosmic, socio-biological and socio-cultural evolution, in terms of a unifying paradigm of self-organization, and the mutual interaction of microstructures (individual atoms, molecules, organisms, etc) with macro- or collective structures (biospheres, ecosystems, societies, and so on). (diagram copyright, Pergamon Press). |
This unit is the partner (see site map) to the pages on deep time; between them, the two units introduce the basic orientation of evolution through time.
The current pages are also more philosophical and speculative than the more specific coverage of Palaeontology and Earth History that is Palaeos' main focus. They represent an exceedingly incomplete overview of some of humanity's attempts to understand the history and the evolution of the life, the Earth, and the universe as a whole, not so much or just or even as science, but as a narrative account, a story of where we are, where we come from, and where we are going; the big picture, in other words. Incorporating human history, the evolution of life and the Earth, and cosmic evolution is what is sometimes referred to as Big History.
There are basically two orientations that can be taken here. One is to follow the sequence of Time, the other Evolution. The word "evolution" is here used in two different contexts. One, systems theory, explains the natural world in terms of the emergence of progressively more complex structures. This is Evolution in the sense of the big picture, aka Cosmic Evolution. The other is biological (darwinian) evolution, which involves the process of natural selection acting in in populations of species, as well as ecosystems and communities. Biological evolution is only one subset of systems theory understanding of evolution. There is also cosmic, galactic, stellar, planetary, mineral, geological, socio-cultural, technological, and other forms of evolution.
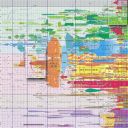
To keep things simple, evolution in the cosmic context, is divided into five emergent and perhaps arbitrary stages: cosmological (itself further dividing into several sub-stages), biological (or socio-biological), mental or psychological or socio-cultural, and a possible future stage, posthumanity, or technological singularity (which assumes technology will continue along an exponential curve, as shown in the colour coded table below:
The Big Picture of Evolution is all about, well, the big picture. It terms of an evolutionary cosmos, this means the emergence of complexity and development and evolution of successive modes of matter, life, consciousness, culture, technology, and more, from the Big Bang till now, and speculation on the future, as illustrated in the above diagram. Obviously, the account of the evolution of life and intelligence is limited here to the Earth, but there is no reason why this things should not have appeared on other worlds and solar systems. If you find it all too irrelevant, eccentric, or speculative, feel free to skip ahead to the Geological timescale page or the story of the meaning of life (or minimal version of said story). MAK110918