 Representative nematomorphs: Gordius (Gordiida) on the left and Nectonema on the right, from Biodidac.
Representative nematomorphs: Gordius (Gordiida) on the left and Nectonema on the right, from Biodidac.| Nematoda | ||
| Nematoda | Nematomorpha |
| Nematodes | Ecdysozoa | Nematoida
└─► |
||
| Scalidophora | None |
Ecdysozoa | Nematoida | Panarthropoda |
By
Christopher Taylor
|
Abreviated Dendrogram
|
Contents
Overview |
The following is reprinted from the Diversity of Life blog by Christopher Taylor (MAK):
Long-term followers of this site may recall this video, linked to over four years ago:
The animal emerging from the unfortunate cricket in the video is a Gordian or horsehair worm, Nematomorpha. Gordian worms spend most of their lives as internal parasites: either of insects (in the freshwater/terrestrial order Gordiida) or of shrimps and crabs (in the marine genus Nectonema). Of the two commonly used vernacular names for this group, 'Gordian worm' refers to the famed Gordian knot, and is derived from the appearance of mating tangles of these elongate animals. 'Horsehair worm' refers to the long-held belief (again, inspired by appearance) that the adult worms developed from horse hairs decaying in water. So persistent was this belief that Leidy felt compelled to report in 1870 on an attempt to generate horsehair worms by this method, explaining that, "I need hardly say that I looked at my horse-hairs for many months without having had the opportunity of seeing their vivification". He also scuttled the fear, which even Linnaeus had reported as fact, that a horsehair worm could inflict a nasty bite on anyone careless enough to handle one. In fact, Gordian worms (being internal parasites absorbing nutrients directly from the host when young and not feeding as adults) do not even possess a mouth. Instead, the males of many species possess a bifurcated tail end, used in copulation, that may have been mistaken for jaws. The complete absence of active feeding has the interesting side effect that adult Gordians may completely lack an internal bacterial flora (Hudson & Floate 2009).
 Representative nematomorphs: Gordius (Gordiida) on the left and Nectonema on the right, from Biodidac. Representative nematomorphs: Gordius (Gordiida) on the left and Nectonema on the right, from Biodidac. |
The primary division within the Nematomorpha between the marine Nectonema and the terrestrial Gordiida is universally agreed upon. The two branches are ecologically, morphologically and molecularly divergent (Bleidorn et al. 2002). Adults of Nectonema have dorsal and ventral double rows of swimming bristles, while those of Gordiida lack bristles (except for, in some species, minute patches of bristles in front of the cloacal opening). Mature adults of Gordiida emerge from their insect host when the latter approaches or enters water. It has been suggested that the worm is able to cause its host to actively seek out water, but it seems more likely that the worm simply causes erratic but non-directional behaviour that may make the host more likely to come into contact with water than if it had remained in its preferred microhabitat (Thomas et al. 2002). Once the host does come close to water as a result of random movement, the worm may be able to induce a last suicidal jump; alternatively, it may simply be that the addled host does not recognise the water as dangerous and makes no attempt to avoid it.
 Female Chordodes wrapped around a stick, laying a white egg string. Photo from the Hairworm Biodiversity Survey. Female Chordodes wrapped around a stick, laying a white egg string. Photo from the Hairworm Biodiversity Survey. |
Once in the water, the adult Gordians will mate with any others present; when multiple adults emerge in close proximity, they may begin mating before they have even finished emerging from their host (Hanelt & Janovy 2004). The females lay their eggs in long strings: one female may lay nearly six million eggs, making them one of the potentially most fecund animals on the planet. The larvae that hatch from the eggs look nothing like their parents, being kind of sausage-shaped with an eversible, spiny proboscis. A larva will find itself an aquatic animal host such as an insect larva or mollusc to burrow into and form a cyst. If the aquatic secondary host is then eaten by a suitable terrestrial primary host (for instance, after an aquatic insect larva matures into a terrestrial adult), the cyst will hatch out and the Gordian will complete its development within the terrestrial host. The Gordian larva may also bypass the secondary host if a primary host drinks water containing Gordian larvae. The larva or mode of transmission of Nectonema remains unknown,but, as Nectonema adults live in the same habitat as their primary host, they probably do not require a secondary host.
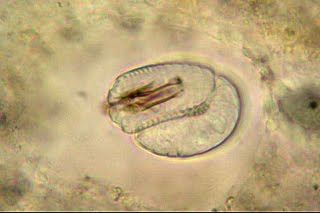 Larva of Chordodes encased in a cyst, from the Hairworm Biodiversity Survey.
Larva of Chordodes encased in a cyst, from the Hairworm Biodiversity Survey. |
Phylogenetically, Gordians have usually been regarded as related to nematodes, with which they share a number of morphological features. However, a molecular analysis by Sørensen et al. (2008) suggested a relationship between Gordians and loriciferans (albeit with support that was not overwhelming). The Gordian larva (which has no equivalent in the direct-developing nematode life-cycle) does bear a vague resemblance to an adult loriciferan, though it is debatable whether the resemblance is more than superficial. Loriciferans have not appeared in many phylogenetic analyses to date, and further investigation is required to establish whether it is the adults or the larvae of the Gordians that hold the clues to their affinities. CKT110509
Links See Encyclopedia of Life
| Ecdysozoa |
text content © 2011 Christopher Taylor; original url .